
一.
B INTRODUCTION 简介
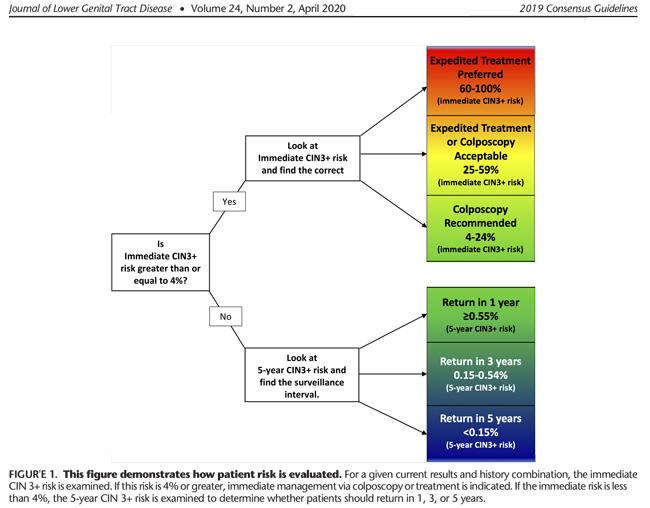
An interim guidance publication providing management recommendations for primary HPV screening was released in 2015.4 This document updates and replaces all previous guidance. The key difference between 2019 guidelines and previous versions is the change from primarily test results–based algorithms (e.g.,Colposcopy is recommended for patients with HPV-positive atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance [ASC-US], low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion [LSIL],etc.) to primarily“risk-based”guidelines (e.gColposcopy is recommended for any combination of history and current test results yielding a 4.0% or greater probability of finding CIN 3+,etc.). See Box 1 for essential changes.
HPV初筛的过渡期指南已于2015年发布,本次发布的2019年指南与之前版本的主要区别在于,从基于检测结果的筛查策略(例如,建议对ASCUS及LSIL进行阴道镜检查)转变为了基于“风险”的筛查策略(例: 如果病史和当前检测结果有4.0%或更高的概率发现CIN 3+,建议使用阴道镜检查”等)。
关于 HPV 阳性分流的问题—同一样本原则
7) All positive primary HPV screening tests, regardless of genotype, should have additional reflex triage testing performed from the same laboratory specimen (e.g., reflex cytology).
• Additional testing from the same laboratory specimen is recommended because the findings may inform colposcopy practice. For example, those HPV-16 positive HSIL cytology qualify for expedited treatment. • HPV 16 or 18 infections have the highest risk for CIN 3 and occult cancer, so additional evaluation (e.g., colposcopy with biopsy) is necessary even when cytology results are negative. • If HPV 16 or 18 testing is positive, and additional laboratory testing of the same sample is not feasible, the patient should proceed directly to colposcopy.
7. 所有初筛 HPV 阳性者,无论基因型如何,均建议用同一实验室标本进行诸如 细胞学分流检测。
- 所有初筛为 HPV 阳性者,无论 HPV 基因型如何,均建议用同一次实验室 样本进行细胞学的分流检测。这一项建议对其同等风险,同等管理的指导意义更 加明确(如 HPV16 阳性细胞学阳性进行阴道镜检查,但如 HPV16 阳性细胞学 HSIL 直接快速治疗)。
- 这一推荐与 2015 宫颈癌筛查异常的临时指南中关于 HPV16/18 可直接转诊阴道镜,非 HPV16/18 需要细胞学分流的建议不同,2019 版指南指出 HPV 阳性,无论 HPV 分型如何都要进行细胞学检查。
- 但 HPV16/18 阳性发生 CIN3 和隐匿性癌的风险较高,因此即使细胞学检查结果为阴性,也有必要进行阴道镜检查。另外如 HPV16/18 阳性,但实验室无法提供对同一样本细胞学的分流检测的条件,患者也可直接转诊阴道镜。
二、风险评估方法
C. GUIDING PRINCIPLES 原则
New 2019 Principles
HPV–based testing is the basis for risk estimation. The term HPV-based testing is used throughout this document and refers to use of either primary HPV testing alone or HPV testing in conjunction with cervical cytology (cotesting). Characteristics of HPV infections, including HPV type and the duration of infection, determine a patient’s risk of CIN 3+.15–18 Although cytology has high specificity (apart from ASC-US) and can be helpful when estimating immediate risk, its lower sensitivity and lower negative predictive value compared with HPV testing reduces its utility for long-term risk prediction.9 The results of HPV tests alone or in conjunction with cytology are used to guide recommendations that allow lengthening of follow-up intervals and deferral of colposcopy for low-risk results. Of note, risk estimates underlying the 2019 management guidelines are based on HPV DNA testing.
HPV检测是风险评估的基础。基于HPV检测指的是单独使用HPV检测或HPV检测与细胞学联合使用。虽然细胞学检测具有较好的特异性,可以用于评估即时风险。但是相比于HPV检测而言,其较低的敏感性及阴性预测值,使其在长期风险预测中的应用价值较低。单独HPV检测或联合检测可用于指导延长随访时间或避免不必要的阴道镜检查。值得注意的是,2019年管理指南的风险评估是基于HPV DNA检测的。
三、 D.METHODS 方法
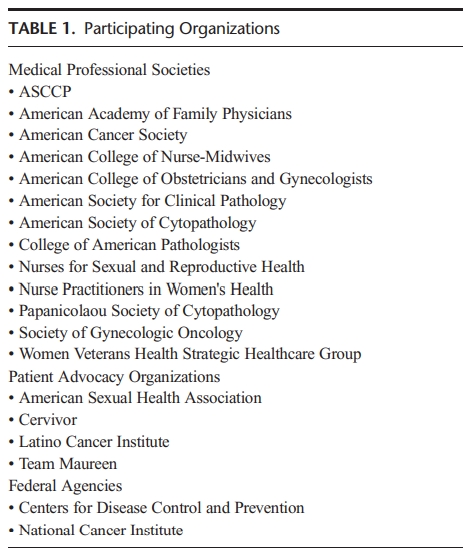
ASCCP sponsored the consensus effort to develop and ratify the guidelines. Stakeholder organizations representing best practice in the United States were identified and invited to participate. These included medical professional societies, patient advocacy groups, and federal agencies integral to cervical cancer screening and management of abnormal results (see Table 1).
ASCCP(美国阴道镜与病理学会)作为指南制定的发起组织,在制定和批准指南的过程中,也邀请了美国具有代表性的社会组织一同制定该指南,详见表1
四、 UPDATES RELATED TO PATHOLOGY REPORTING AND LABORATORY TESTS 病理报告及实验室检测
F.2 Updated Management of Primary HPV Screening (Replaces Interim Guidance)
Rationale: The US FDA approved the cobas HPV test (Roche, Indianapolis, IN), in March 2014, and the Onclarity HPV Test (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ), in April 2018, for primary HPV testing for screening for patients 25 years or older.60 Both these tests offer and are approved for partial HPV genotyping. Use of primary HPV screening will likely increase in the future, as it is more effective than screening with cytology alone and performs similarly to and with lower costs than screening with cotesting.
2014年3月及2018年4月,美国FDA先后批准了Roche cobas HPV ,BD Onchlarity HPV可用于25岁以上女性宫颈癌初筛。这两种检测都提供部分HPV基因分型。鉴于HPV初筛效果优于单独细胞学筛查,并等同于联合筛查。未来,HPV初筛会越来越被广泛地应用。

封面图.png)









封面图.jpg)